page title goes here Risk Assessment
SPRG Home
Welcome
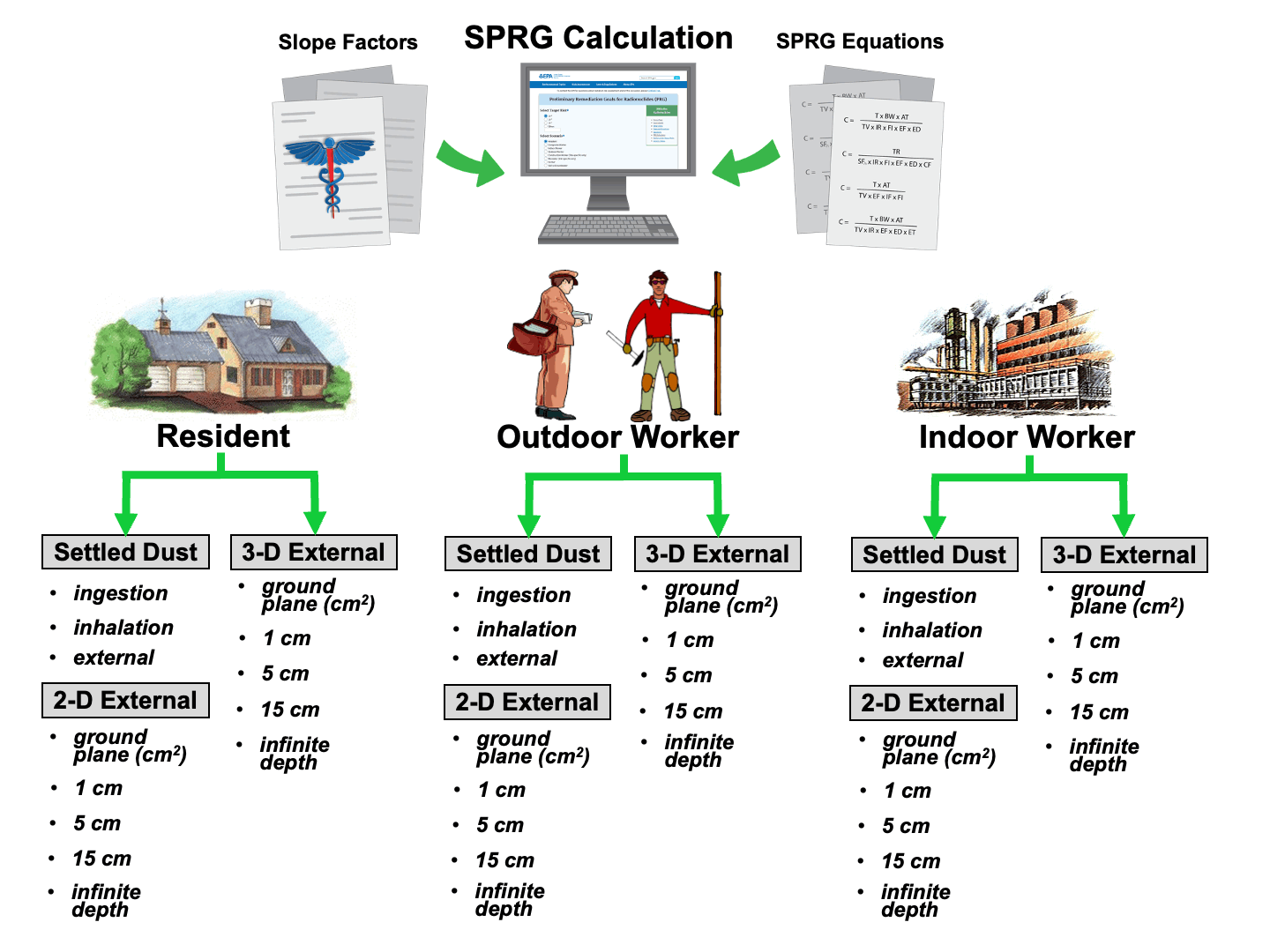
Welcome to the EPA's "Preliminary Remediation Goals for Radionuclides on Outdoor Surfaces at Superfund Sites" (SPRG) Download and Calculator website. The recommended SPRGs on this website are preliminary remediation goals (PRGs) for contaminated outdoor hard surfaces, such as building slabs, outside building walls, sidewalks, and roads. PRGs are addressed in the NCP and EPA CERCLA guidance. Typically, PRGs are risk-based, conservative screening values to identify areas and contaminants of potential concern (COPCs) that may warrant further investigation.
This tool presents recommended risk-based SPRGs calculated using default input parameters and the latest toxicity values. In addition, users are able to modify the input parameters to create site-specific SPRGs to meet the specific site needs, considering factors related to the underlying exposure scenarios, pathways, and routes. To learn more about the use of these recommended SPRGs, please see further guidance located in the "User's Guide", "What's New", 'FAQ", and "Download Area" links. Below is a general description of SPRG use involving radionuclides. The EPA has prepared a fact sheet for the general public that describes SPRG uses, SPRG calculator operation, and land uses available for assessment. Additionally, this fact sheet describes the SPRG and SDCC calculators in greater detail for EPA staff. The OSWER Directive, Superfund Radiation Risk Assessment: A Community Toolkit was also developed by the EPA to help the public understand more about the risk assessment process used at Superfund sites with radioactive contamination.
The SPRG calculator results were previously verified. The documentation from these may be seen on the Internal Verification and External Verification pages. The SPRG calculator was previously peer reviewed, and the documentation of those peer reviews may be seen here. A comparison review that focused on describing the default parameters in various models may be found here. The Superfund approach of consistency between its risk assessments for chemical and radiological contamination, and its use of slope factors/risk coefficients to develop cleanup levels, has received outside high level risk management/policy and scientific review which is discussed here.
Introduction
The purpose of this recommended SPRG calculation tool is to assist risk assessors, remedial project managers, and others involved with risk assessment and decision-making at sites with contaminated outdoor hard surfaces, such as buildings, slabs, outside building walls, sidewalk, and roads.
This website was updated after new EPA guidance was issued. The website was initially made available for use in a transmittal memo entitled "Distribution of Superfund Preliminary Remediation Goals for Radionuclides in Outdoor Surfaces (SPRG) Electronic Calculator", January 16, 2009.
Preliminary Remediation Goals
This recommended calculator is based on Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume I, Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part B, Development of Risk-based Preliminary Remediation Goals) (RAGS Part B). RAGS Part B provides guidance on using EPA toxicity values and exposure information to calculate risk-based SPRGs. Initially used at the scoping phase of a project using readily available information, risk-based SPRGs generally are modified based on site-specific data gathered during the RI/FS study. SPRG development and screening should assist staff in streamlining the consideration of remedial alternatives. The recommended radionuclide-specific SPRGs in this calculator are from two general sources: (1) concentrations based on potential Applicable or Relevant and Appropriate Requirements (ARARs) and (2) concentrations based on risk assessment. ARARs include concentration limits set by other environmental regulations, such as Safe Drinking Water Act maximum contaminant levels (MCLs). The second source for SPRGs, and the focus of this recommended database tool, is risk-based calculations that set concentration limits using toxicity values under specific exposure conditions.
The recommended approach for developing remediation goals is to identify SPRGs at scoping, modify them as needed at the end of the investigation or during the remediation phase based on site-specific information from the baseline risk assessment, and ultimately select remediation levels. In order to set radionuclide-specific SPRGs in a site-specific context, however, assessors should answer fundamental questions about the site. Information on the radionuclides that are present onsite, the specific contaminated media, land use assumptions, and the exposure assumptions behind pathways of individual exposure normally is necessary in order to develop radionuclide-specific SPRGs. This calculation tool provides a recommended approach for modifying the recommended standard default SPRG exposure parameters to calculate site-specific SPRGs.
Once this database tool is used to retrieve standard SPRGs or calculate site-specific SPRGs, it is important to clearly document the equations and exposure parameters used in the calculations. Discussion of the assumptions that go into the SPRGs calculated should be included in the document where the SPRGs are presented, such as a Remedial Investigation (RI) Report or Feasibility Study.
This recommended database tool presents standardized risk-based SPRGs and variable risk-based SPRG calculation equations for radioactively contaminated outdoor hard surfaces, such as building slabs, outside building walls, sidewalks and roads. Recommended SPRGs are presented for resident and worker exposure. The recommended risk-based SPRGs for radionuclides are based on the carcinogenicity of the analytes. The suggested standardized SPRGs are based on default exposure parameters and incorporate exposure factors that present RME conditions. This recommended database tool presents SPRGs in both activity per area and mass per area units.
This website combines current cancer slope factors (SFs) with "standard" exposure factors to estimate contaminant concentrations in environmental media (soil and water) that are protective of humans (including sensitive groups) over a lifetime. SFs used are provided by the Center for Radiation Protection Knowledge. The main report is Calculations of Slope Factors and Dose Coefficients and the tables of slope factors are in a separate appendix.
Sufficient knowledge about a given site may warrant the use of site-specific assumptions that may differ from the defaults. Exceeding a PRG usually suggests that further evaluation of the potential risks is appropriate. The PRG concentrations presented on this website can be used to screen pollutants in environmental media, trigger further investigation, and provide initial cleanup goals, if applicable.
Related CERCLA Calculators and Guidance
It should also be noted that calculating a SPRG addresses neither human radionuclide dose or noncancer toxicity nor potential ecological risk. Of the radionuclides generally found at CERCLA sites, only uranium has potentially significant noncancer toxicity. When assessing sites with uranium as a contaminant, it may also be necessary to consider the noncancer toxicity of uranium using other tools, such as EPA's Regional Screening Levels (RSLs) for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites electronic calculator for uranium in soil, water, or air and the WTC for uranium inside buildings. EPA's PRG Calculator should be used to assess radionuclide cancer risk in soil, water, and air and the BPRG Calculator for radionuclide cancer risk inside buildings. EPA's DCC Calculator should be used to assess radionuclide dose for soil, water, and air, BDCC Calculator for radionuclide dose inside buildings, and the SDCC Calculator for radionuclide dose for hard outside surfaces. For sites where vapor intrusion may be of concern, the EPA's Vapor Intrusion Screening Levels (VISL) Calculator for chemicals should be consulted and for sites with radon, the Radon Vapor Intrusion Screening Level (RVISL) Calculator for Radionuclide Contaminants at Superfund Sites should be consulted. Similarly, some sites with radiological contaminants in sensitive ecological settings may also need to be evaluated for potential ecological risk. EPA's guidance "Ecological Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Process for Designing and Conducting Ecological Risk Assessment" contains an eight step process for using benchmarks for ecological effects in the remedy selection process. The CPM Calculator converts screening levels, whether risk-, dose-, or ARAR-based, from units of pCi into counts per minute (cpm).
Below is a table that summarizes the existing EPA online calculators for assessing risks from chemicals and radionuclides at Superfund sites.
| Media Addressed | Chemical Risk | Radiological Risk | Radiological Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human Health Protection | |||
| Soil, Water, Air, Biota, Soil to Groundwater | RSL | PRG | DCC |
| Inside Buildings (Dust, Air, Fixed Contamination) | WTC | BPRG | BDCC |
| Outside Buildings (Dust, Air, Fixed Contamination) | SPRG | SDCC | |
| Vapor Intrusion (Air, Soil Gas, Groundwater) | VISL | RVISL | RVISL |
| Ecological Health Protection | |||
| Soil, Sediment, Surface Water, Biota | ECO-RAGS | ||
| Conversion of Screening Levels to Counts Per Minute | |||
| Soil, Concrete, Wood, Glass, Steel, Drywall | CPM | CPM | CPM |
